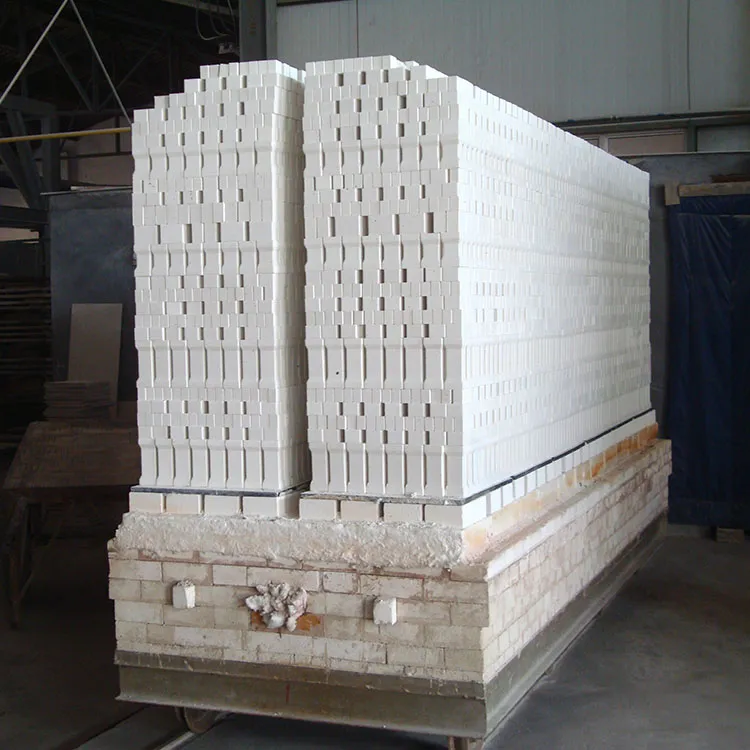

In the dry quenching system of the metallurgical industry, the selection of refractory materials has always been a challenging task. The operating conditions of dry quenching devices are characterized by frequent high - temperature fluctuations and significant differences in performance requirements at different connection stations. This article will delve into the limitations of traditional high - alumina bricks and introduce a new type of mullite refractory brick that can significantly improve service life.
Traditional high - alumina bricks have long been used in dry quenching systems. However, in an environment with severe high - temperature fluctuations and frequent start - stops, they are prone to damage. For example, in a certain metallurgical enterprise's dry quenching system, the traditional high - alumina bricks in the inclined channel area needed to be replaced every 1.5 years on average. The main reasons for their damage are as follows. First, high - alumina bricks have poor thermal shock resistance. When the temperature changes rapidly, large internal stress will be generated, leading to cracks. Second, under the influence of chemical corrosion and mechanical impact in the high - temperature environment, the structure of high - alumina bricks will gradually be destroyed.
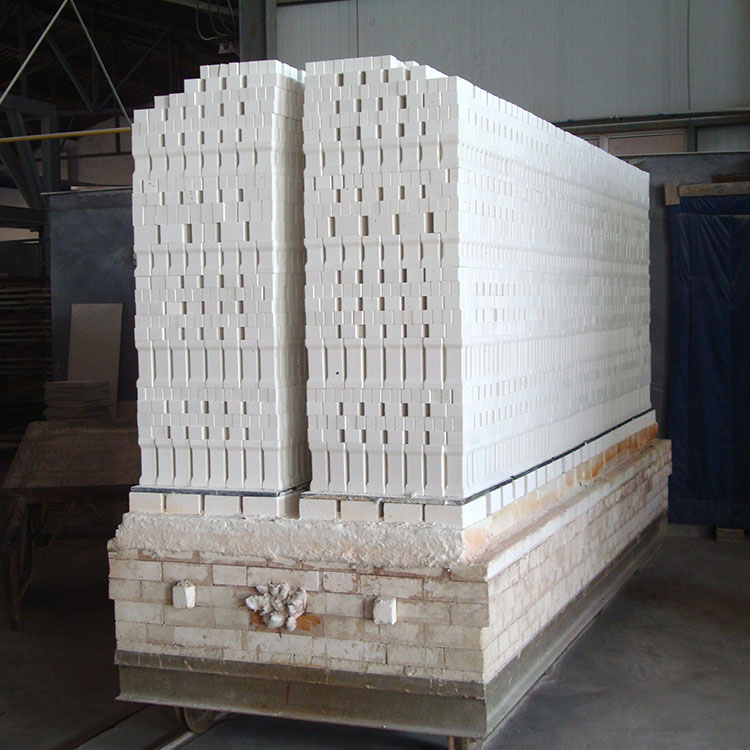

The new high - purity mullite refractory bricks use a fine - crystal strengthening technology and a composite structure design. This new type of brick has a much higher thermal shock resistance than traditional high - alumina bricks. In a practical project, after using new mullite refractory bricks in the cooling chamber of a dry quenching system, the service life was extended from the original 2 years to more than 5 years. The fine - crystal strengthening technology can effectively disperse the internal stress generated by temperature changes, and the composite structure can further enhance the overall strength of the brick.
Let's take a look at the application scenarios of new mullite refractory bricks in different areas. In the inclined channel area, the new bricks can better withstand the high - temperature flue gas scouring and temperature fluctuations. In the cooling chamber, they can maintain stable performance under long - term low - temperature and high - temperature alternating conditions. At the coke discharge port, the high wear - resistance of the new bricks can effectively resist the abrasion of coke.
In addition to the material itself, construction also plays a crucial role in the performance of refractory bricks. For example, controlling the masonry joints and setting expansion joints properly can significantly improve the thermal shock resistance of the refractory lining. In a project, by strictly controlling the masonry joint width within 2mm and setting expansion joints at appropriate intervals, the thermal shock resistance of the refractory lining was improved by about 30%.
Let's take a look at a detailed construction case. In a large - scale metallurgical enterprise's dry quenching project, through strict construction management and the use of new mullite refractory bricks, the service life of the entire dry quenching system was significantly extended, and the production efficiency was improved by 10%.

In conclusion, traditional high - alumina bricks have obvious limitations in dry quenching systems. The new high - purity mullite refractory bricks, with their fine - crystal strengthening technology and composite structure, combined with proper construction techniques, can effectively improve the service life of dry quenching systems. For metallurgical enterprise technology leaders, choosing the right refractory materials and ensuring high - quality construction can enhance the stability of equipment and bring better economic benefits.
If you are interested in our new high - purity mullite refractory bricks, please contact us at [Contact Information]. We will provide you with more detailed technical information and application cases.

